Over thirteen yearsexperience in the industry
We can offer aMarket comparison
Accepted bymajority of high street banks
Recognised byUK Finance
Climate Change – the Impact on Housing and Construction
With the impacts of Climate Change becoming more and more apparent, the UK construction industry is evolving to keep up to pace with the changes required to contribute toward a more sustainable industry.
 By the end of the 21st century, all areas of the UK are predicted to be warmer (1), with UK Summers seeing the greatest rise in temperatures, and the winters seeing a 30% increase in rain. Nearly 5.2 million properties are at risk of being flooded every year (2), equating to 1 in 6 properties. By 2050, this number could double.
By the end of the 21st century, all areas of the UK are predicted to be warmer (1), with UK Summers seeing the greatest rise in temperatures, and the winters seeing a 30% increase in rain. Nearly 5.2 million properties are at risk of being flooded every year (2), equating to 1 in 6 properties. By 2050, this number could double.
The built environment contributes to 25% of the UK’s total greenhouse gas emissions annually, with this in mind the UK government has started to examine the ways in which emissions can be reduced whilst still reaching the 300,000 homes target annually.
Here at Granite, we have been looking into some ways developers can ensure properties are attempting to reach the Net Zero Carbon target.
What is a Net Zero Carbon property/build?
In principle, a Zero Carbon house produces zero or negative CO2 emissions. They aim to maximise energy efficiency and maintain renewable energy. It is important to note that location plays a big part in suitability for generating and accommodating renewable energy.
Advantages
- Greater demand for energy-efficient properties (3) – with profits averaging 20% more than for an existing property
- Lower carbon footprint
- Reduction in waste
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
- Savings over time
Disadvantages
- High initial cost of sustainable build/heating
- Energy Supply may differentiate depending on the weather conditions
- Funding from lenders may be difficult due to the relative newness of methods/technology
- Construction methods can be complex and specialist builders may be required
Air Source Heat Pumps
- Air source heat pumps absorb heat pumps from the outside air into a liquid refrigerant at a low temperature. By using electricity the pump compresses the liquid to release its stored heat. The Heat is then sent to your radiators or underfloor heating. This can then be stored in the hot water cylinder.
- According to Savills latest report, in 2021 the UK installed 1.48 heat pumps per 1,000 households, however, countries such as Norway installed 49.77 heat pumps per 1,000. Despite the increased cost of a Heat Pump, compared to a Gas boiler they are 300-400% more efficient per Kilowatt of Electricity. It is also possible to run your ASHP using Solar panels
- A typical ASHP costs between £7,000 to £13,000 but some families are eligible for a £5,000 grant.
Ground Source Heat Pump
Ground source heat pumps work by transferring heat from the ground outside your home to heat your radiators, underfloor heating, and hot water. Here’s how they operate:
- Heat Absorption: A mixture of water and antifreeze circulates through a loop of pipe buried in your garden or outdoor space, absorbing heat from the ground.
- Heat Transfer: The fluid passes through a heat exchanger into the heat pump, raising its temperature.
- Heat Conversion: The heat is then transferred to water for heating purposes.
- Refrigeration Process: The fluid continues its circuit back to the submerged pipework to repeat the cycle.
- Typical Costs: Basic pump from £2,000 to £15,000. Installation from £16,000 to £45,000
Passivhaus Builds
- Passivhaus houses are based on the concept of providing brilliant indoor air quality and temperature using very little energy for heating/cooling.
- They aim to maintain a constant temperature by retaining heat from the sun
- They often have triple-glazed windows, Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery system attached
- The Average cost of a Passivhaus is 5-10% more than a conventional build (4), however, due to the high standard of build, fewer repairs and replacements are required, leading to fewer callbacks for developers.
- Passivhaus tend to value 7% higher than standard builds,
Solar Panels
- The Average cost of Solar panels is around £6,500 for a 4kwp system, with the batteries for storing the electricity, costing anywhere between £1,200 to £6,000.
- An average 4kwp can save up to 675kg of Carbon emissions annually (7)
- The Payback time for Solar Panels by January 2023’s rates, will be 3.75 years.
- Solar panels are considered ‘Permitted developments’ and often do not require planning permission.
- The Average system will require 25m2 of roof
Bamboo
- Bamboo is a very sustainable alternative to Timber, and researchers argue stronger than Steel (9).
- Bamboo can grow in areas where no other plants can and grows much faster than Timber.
- Most Bamboo species can survive UK winters, with no additional care required.
- Bamboo tends to be more cost-effective than traditional materials
What is the government doing to push developers towards Net Zero Carbon?
In June 2022, the government implemented changes to the Building Regulations (5) in favour of building Net Zero Carbon properties, the changes are as follows;
- All new homes must produce 31% less carbon emissions.
- New non-domestic builds will need to produce at least 27% less carbon emissions
- New metric for measuring energy efficiency
- New minimum efficiency standards have been provided
- New and replacement heating systems in both domestic and non-domestic builds must have a maximum flow temperature of 55 Degrees.
- Existing non-domestic buildings must improve the efficiency of heating and hot water boiler systems.
- Background trickle vents have been recommended for non-domestic buildings along with a new requirement for CO2 monitors in all offices.
The Green Deal
The Green Deal (6) is a scheme set up by the UK government to enable homeowners to benefit from energy-saving improvements. Any Household within England, Scotland or Wales with an electricity meter can benefit from the scheme.
An assessment of energy usage within your home will be undertaken by a Green Deal Assessor (8) and will evaluate how you could benefit from the improvements. This could include;
- Replacing windows and doors
- Draught proofing
- Wind power or solar panels
- Insulation
- Upgrade to lighting
- Double glazing
A loan is granted by a chosen provider and is paid back through a charge added to your electricity bill. The Green Deal stays with the property so if you move you no longer make repayments. The Annual repayments on the loan shouldn’t be more than the savings you would make from benefitting from the improvements.
With this in mind, the Construction sector is becoming more aware of the need for change. It appears the Government are clearly aware of the severity of Climate Change, offering continuing support to the Construction Industry.
For further information please contact Ed, Kelly & Rob on Tel: 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk/ rob@granitebw.co.uk
References
- Met Office
- Gov
- Property Reporter
- Homebuilding
- Gov
- Green Deal Gov
- Carbon Emissions
- Green Deal Assessor
- Bamboo
STARTING YOUR SELF BUILD
So you now have your planning permission for your self-build – great news! Before you get started, there are still several critical stages to complete before you give the builders the go-ahead. Read on to ensure a smooth running project and that your property is covered in its entirety.

Planning Conditions:
- Discharging Planning Conditions will require another application to the planning department and can take up to 12 weeks to discharge.
Finding the Right Contractor:
- Check references on their financial standing
- Visit current and previous projects
- Word of mouth referral is a good start
- Do not make large upfront payments
Building Regulation Drawings:
- You will need your architect to prepare drawings for building regulation submission and submit them to the local authority for approval.
Project Managing the Build:
- A project manager handles the planning conditions, building regulations and ensures the work is completed on budget, on time and that all planning permissions, site insurances and warranties are in place.
- If you take on this role yourself it can be very time-consuming and could cost you a lot more time and money.
- A Chartered Surveyor can manage the project for you and will avoid mistakes and overspending.
Building Warranty:
- You will need to put a 10-year structural warranty/latent defects insurance in place at the beginning of the construction process.
- Granite Building Warranties will provide a number of options for both self-builders or developers and provide a very professional service. These are the self build warranty and the commercial building warranty.
Building Control:
- Building regulations are minimum standards for design, construction and alterations and apply to every building project.
- You will need to engage the services of Building Control. This can be the local authority or an approved inspector and they will need to inspect at the key stages, which are: Foundations, DPC, Roof plate, Roof on, First & Second fix and Completion.
- Completions certificates are issued upon completion of the build and no sale can take place until they are issued.
Site Insurance:
- Site insurance is essential for all developments and can be arranged in conjunction with the warranty. Site insurance will cover you against theft of tools/plant, damage/fire to the building and third-party liability.
The Way Forward:
Granite Building Warranties Ltd can assist you with all insurance requirements for your build and will take the worry and hassle out of the project.
For further information please contact Ed, Kelly & Rob on Tel: 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk/ rob@granitebw.co.uk
TIMBER FRAME OR TRADITIONAL BRICK & BLOCK?
Key differences in building with a timber frame or a traditional brick and block:
Timber Frame 
Speed of Construction: A prefabricated timber frame can be erected faster than a traditional build.
Costs: The cost may be higher, however, the speed of the build may off set this extra cost.
Quality: The offsite fabrication ensures greater accuracy and precision of build.
Energy Efficiency: More energy efficient and the build quality will enable air-tight buildings with low carbon emissions and significantly reduced energy costs.
Acoustics: Timber frame structures may not achieve the same acoustic ratings as a traditional build.
Lifespan: Often thought to be more prone to rot and fire risk and therefore have a shorter lifespan. However, if timber is correctly treated this is not the case.
Brick and Block 
Speed of Construction: More time and labour intensive as work carried out on site by builders and weather can be a delay factor.
Costs: Despite additional time, the costs may be similar in terms of materials and labour.
Quality: If plans are poor, there can be discrepancies with plans and difficulties when fitting windows, stairs etc if the walls are not plumb. Differentials of up to 10mm have been known! Ensure good contractors and architects are used.
Energy Efficiency: Traditional brick & block requires high levels of insulation for energy efficiency; however, masonry is better for heat retention. Improvements are being made in energy-efficient construction methods for traditional brick and block.
Acoustics: Solid masonry walls and concrete floors will produce better acoustic results.
Lifespan: Traditional construction will last longer if built properly and in line with Building Regulations.
For more information please contact Ed or Kelly on:
Tel: 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk
SIZEWELL C DECISION DELAYED AGAIN

The deadline for planning consent on the proposed new nuclear power station at Sizewell in Suffolk has been delayed again. A decision had been expected on 7th July but has been pushed back to 20th July 2022 following the collapse of the UK Government last week.
The reason for the new deadline, according to Paul Scully Minister for London and Parliamentary Under Secretary of State (Minister for Small Business, Consumers and Labour Markets) is “to ensure there is sufficient time to allow the Secretary of State to consider the proposal” and that it “is without prejudice to the decision on whether to grant or refuse development consent”.
The French energy company EDF are planning to build Sizewell C but are in the process of being re-nationalised by the French government because of financial difficulties and their own nuclear power plans.
The UK Government pledged £100million to the Sizewell C project back in January to support the development but local groups are strongly against the new power station as it sits in an area of significant special scientific interest and natural beauty and adjacent to the RSPB Minsmere site.
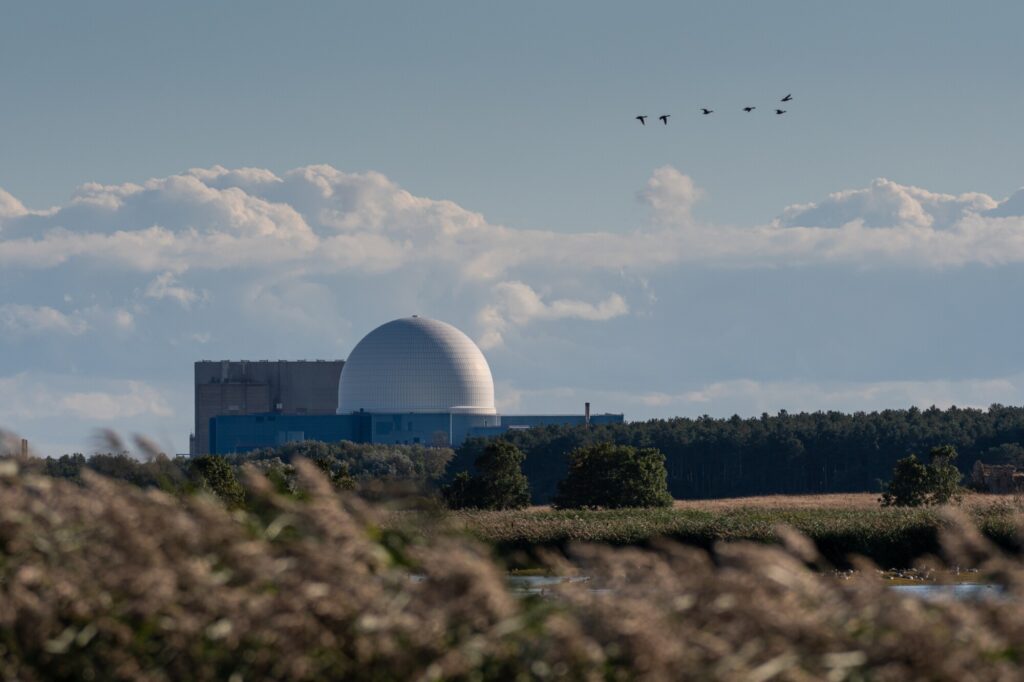

Alison Downes, of campaign group Stop Sizewell D, said that she “hopes that announcements of EDF’s re-nationalisation have given ministers pause, especially when EDF’s parlous finances are at least in part down to their disastrous track record at building the type of reactors proposed for Sizewell C.”
EDF has a history of problems building these power stations, many coming in significantly over budget and way behind schedule.
However, the Government is keen to push ahead as the Suffolk station is part of a fleet of new nuclear power plants that form a key part of the government’s energy strategy, along with offshore wind and hydrogen.
For more information, please contact Ed or Kelly on 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk.
CHANGES IN BUILDING REGULATIONS: WHAT THEY ARE AND HOW THEY IMPACT ON YOUR BUILDING PLANS
The Government’s new changes to Building Regulations will come into force on 15th June 2022.
These are the first steps towards the Future Homes Standard, which is designed to make all new builds net carbon zero by 2025 and significantly improve energy and efficiency in existing buildings.
The key changes for New Homes will be:
- A 30% cut in emissions from new homes
- A 27% cut in non-domestic new builds including offices and shops
- Improvement of heating and lighting efficiency.
- A new Building Regulation to mitigate the risk of overheating in new homes including maximum limits to the amount of glazing on new residential buildings
- New homes will adopt the Fabric Energy Efficiency Standard to measure energy efficiency
- There will be a maximum flow temperature requirement of 55°C for new and replacement heating systems

The key changes for Existing Buildings will be:
- New minimum standards for fabric efficiency – there will be a new efficiency metric for the whole house calculation method for new extensions
- There will be a requirement for new or replacement heating system designs to accept low-carbon heating in future, including integrating the latest Ecodesign appliance benchmarks.
There is also new information regarding infrastructure for electric vehicles and all new homes will be required to have charging points for electric vehicles.
The transition period – 15 June 2022 until 15 June 2023.
Buildings currently in the planning process where documents have been submitted and approved before the 15th of June 2022 will still be considered under the previous regulations, providing work beings before the 15th of June 2023.
For work not requiring applications, the new regulations will come into force from the 15th of June 2022.
For more information, please contact Ed or Kelly on 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk.
CHANGES IN BUILDING REGULATIONS: THE COST IMPLICATIONS OF THE NEW RULES

The Government’s new changes to Building Regulations will come into force on 15th June 2022, although a transition period will be in place until 15th June 2023 to enable plans already submitted and approved to continue with the existing regulations.
However, all new planning submissions will be subject to the new regulations and this will impact further on the already spiralling costs of building work.
Developers estimate the new regulations will cost the industry more than £10 billion over the next 70 years.
The higher cost of the new greener technologies required will impact upon the overall cost of the build. Increased insulation, ventilation, thermal heat pumps, reduced glazing and electric charging points will all add to the budget.
Carbon emissions targets will be more stringent, meaning that thermal elements such as walls, floors, and roofs will require more insulation and many more renewable technologies such as Solar Panels will be required.
Better insulation equates to larger cavities and, therefore, increased amounts of installation which will add to the costs. Combine this with the need to build slightly bigger in order to keep the same internal footprint and all material costs will increase.
The industry in principle is in favour of the move towards more sustainable, carbon-neutral, energy-efficient buildings, but getting the big developers to change their long-held attitude to finding the cheapest building solutions may prove a challenge.
For more information, please contact Ed or Kelly on 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk.
WHAT IS STRUCTURAL FAILURE?
The definition of structural failure:
Loss of the load-carrying capacity of a component or member within a structure or of the structure itself. Structural failure is initiated when the material in a structure is stressed to its strength limit, thus causing fracture or excessive deformations.
 The causes of a building collapse or failure can be various including bad design, faulty construction, foundation failure, extraordinary load, or a combination of these factors.
The causes of a building collapse or failure can be various including bad design, faulty construction, foundation failure, extraordinary load, or a combination of these factors.
Examples of structural components in a building would include:
- Wooden or steel I-beams – which can fail when an imposed load exceeds the capacity of the beam
- Reinforced concrete will suffer if the mix and raw materials used are incorrect
- Foundation failures can occur when there is uneven soil settlement and uneven loading, moisture in the subsoil and insufficient compaction.
All of the above reinforces the need for structural warranty insurance on new buildings, extensions and conversions.
As specialists in structural warranty and latent defect insurance, please contact us for further information:
Ed or Kelly on 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk.
AS IF BY MAGIC – NEW HOMES THAT WILL RISE ABOVE THE FLOODS
It is estimated that flooding costs Britain £1.3 billion a year, with one in six homes now in flood zones and the increased risk of flooding up by 56% due to the effects of climate change.
The FloodSafe house is a prototype being developed by Hadley Group and Floodjack International to mitigate against flooding and protect both homes and lives.
Andrew Parker, a former builder and now Director of Floodjack International, came up with the idea of the jack system after a friend lost everything due to flooding and the Hadley Group, who build modular homes with steel frames, repurposed one of their steel frames to help develop the FloodSafe house prototype.
 Water sensors under the house trigger the mechanical jacks to lift the house up to 1.5m within 15 minutes. The system continues to track the water level keeping the house 15cm above water until it is safe to return to the ground. There is also a built-in home battery allowing the house to remain fully functional for 3 days off-grid if services should be lost in the storm.
Water sensors under the house trigger the mechanical jacks to lift the house up to 1.5m within 15 minutes. The system continues to track the water level keeping the house 15cm above water until it is safe to return to the ground. There is also a built-in home battery allowing the house to remain fully functional for 3 days off-grid if services should be lost in the storm.
The FloodSafe house is more expensive to build than the same modular home without the flood avoidance system but as flood land is cheaper to buy it can work out cost-effective.
Now there is a visible working house people are starting to believe it is possible and flood jacks should become commercially available very quickly according to Mr Parker.
“If people see a real house going up and down ..….they start believing it.”
Across the world, different technologies are being developed to deal with flooding from watertight inflatable barriers for doorways in Ireland to amphibious buildings that float in the Netherlands.
As LABC, who represent local authority building control teams, have also approved the FloodSafe house in principle, it is looking quite possible that we will see houses literally rising above the flood water here in the not too distant future.
For further information, please contact Ed or Kelly on 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk.
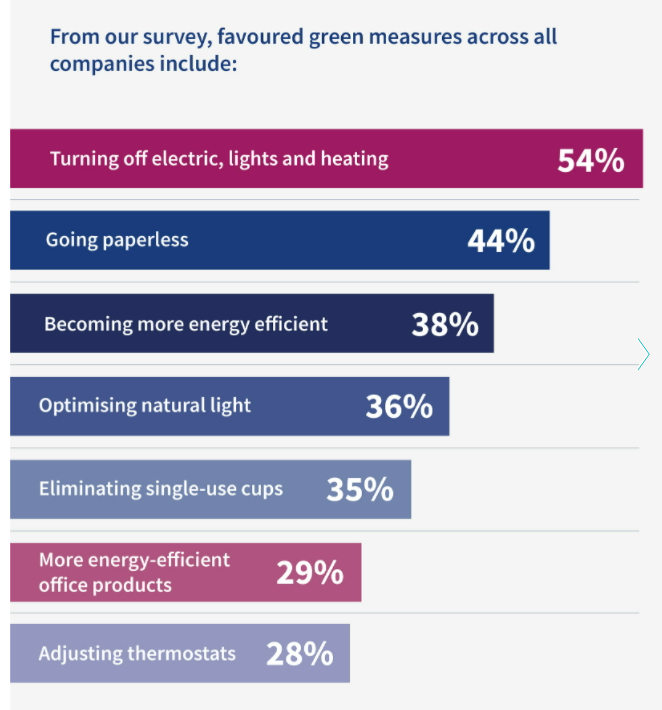
Companies Reluctant to Pay a Higher Price for Greener Offices
According to a recent occupiers’ survey conducted by YouGov and Irwin Mitchell, businesses are less keen to invest money in increasing the green credentials of their offices. They are looking more to changing habits within the workplace to offset their carbon footprint.
Larger businesses are the most likely to invest in ways to reduce their environmental footprint; including paying more for a greener office space (15%), having a sustainability team (36%) and investing in Property Technology (30%). A further 29% said they would accept increased rent if there was a financial incentive to do so, such as reducing service charge or energy costs.
The smaller businesses, however, feel that adopting greener practices is costly at a time when they are looking to save money.
Changing habits seem the most popular way of reducing the environmental impact of the office. Turning off lighting, heating and electric when offices are unused is the most popular option.
It appears to be the belief that small changes from employees across the company can have a big impact on environmental issues. This is a more favoured approached than investing money into future technologies.
According to Larry Fink of Blackrock, however, ignoring the green agenda is a perilous decision that will leave behind the companies that don’t adapt: “Decarbonising of the global economy is going to create the greatest investment opportunity… accompanied by enormous job creation for those that engage in the necessary long-term planning.”
Overall, however, it would seem that green decisions are still being driven by financial considerations for the majority of companies.
For further information, please contact Ed or Kelly on 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk.
SAVILLS AUCTION HITS SEVEN YEAR HIGH
 Savills’ live streamed auction on 2nd March 2022 raised £53 million, the highest total since March 2015.
Savills’ live streamed auction on 2nd March 2022 raised £53 million, the highest total since March 2015.
Strongest demand was for development land, residential properties in need of refurbishment and investment sites.
One single lot attracted over 70 bids in 45 seconds.
A mid-terrace in Dartford, Kent with a guide price of £120,000 sold, after much activity, for £271,000.
The highest value lot, a detached property in West Ealing, sold for £2.3 million.
According to Jeremy Lamb, Auction Director for Savills: “Buyer demand has been strong for quite some time, but there was definitely a sense with this sale that people were extremely keen to transact and invest in the assets on offer.”
It would seem that property remains a strong market for investment.
For further information, please contact Ed or Kelly on 01284 365345 or email ed@granitebw.co.uk / kelly@granitebw.co.uk.
Copyright © 2024 Granite Building Warranties
Supported by Fox 360 Ltd
Granite Building Warranties Ltd is an Appointed Representative of Richdale Brokers & Financial Services Ltd which is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority.
Granite Building Warranties is a company registered in England and Wales (Company Number 11497543) with its registered office at 1st Floor, 5 Century Court, Tolpits Lane, Watford, WD18 9PX